반응형
# Q-learning 알고리즘
#
# Created by netcanis on 2023/08/22.
#
# 5x10 크기의 그리드 월드 환경에서 Q-learning 알고리즘을 실행하는 간단한 예시입니다.
# 에이전트는 상, 하, 좌, 우로 움직이며 목표 지점에 도달하는 최적의 경로를 학습
# 매 에피소드마다 이동 경로 및 순서를 실시간으로 출력
# 에피소드 100의 배수마다 이동경로 및 순서 출력
# 경로 횟수가 적을수록 높은 보상
# 에피소드가 증가할수록 탐험보다 활용을 선택하도록 개선.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 그리드 월드 환경 설정
# 0: 빈공간, 1: 벽, 2: 목적지, (0,0)): 시작위치
grid = np.array([[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2]])
# Q-learning 매개변수
NUM_STATES = np.prod(grid.shape) # 상태 공간 크기 (5x6=30)
NUM_ACTIONS = 4 # 상, 하, 좌, 우
# hyperparameter
EXPLORATION_PROB = 0.2 # 탐험율 - exploration(탐험)과 exploitation(활용) 사이의 균형을 조절.
LEARNING_RATE = 0.1 # 학습률 - 경사 하강법 등 최적화 알고리즘에서 가중치 업데이트에 사용되는 학습률.
DISCOUNT_FACTOR = 0.99 # 할인율 - 강화 학습에서 미래 보상을 현재 보상보다 얼마나 중요하게 고려할지를 조절하는 요소.
NUM_EPISODES = 1500 # 강화 학습에서 에피소드 수
# Q 함수 초기화
Q = np.zeros((NUM_STATES, NUM_ACTIONS))
# 상태 인덱스 계산 함수
def state_index(state):
return state[0] * grid.shape[1] + state[1]
# 그래프 초기화
plt.ion()
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
episode_rewards = []
# 시작 위치 설정
start_position = (0, 0)
print("begin_position :", start_position) # (0, 0)
# 타겟 위치 설정
target_position = np.argwhere(grid == 2)[0]
print("target_position :", target_position) # (4, 9)
# 그리드 월드 환경 출력 함수
def plot_grid_world(state, path=[]):
plt.imshow(grid, cmap="gray", interpolation="none", origin="upper")
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
if path:
path = np.array(path)
plt.plot(path[:, 1], path[:, 0], marker='o', markersize=4, linestyle='-', color='green')
for i, pos in enumerate(path):
plt.text(pos[1], pos[0], str(i + 1), ha="center", va="center", color="orange", fontsize=14)
plt.text(state[1], state[0], "A", ha="center", va="center", color="red", fontsize=16)
plt.text(grid.shape[1] - 1, grid.shape[0] - 1, "B", ha="center", va="center", color="green", fontsize=16)
def choose_action(state, epsilon):
if np.random.rand() < epsilon:
return np.random.choice(NUM_ACTIONS)
return np.argmax(Q[state_index(state)])
# Q-learning 알고리즘
for episode in range(NUM_EPISODES):
print(f"Episode: {episode + 1}/{NUM_EPISODES}")
state = tuple(start_position)
total_reward = 0
path_taken = []
# Decaying exploration
# 에피소드가 증가할 수록 탐험하는 비율을 쇠퇴시킨다.(원래 탐험율의 절반으로 줄인다)
epsilon = EXPLORATION_PROB + (EXPLORATION_PROB / 2 - EXPLORATION_PROB) * (1.0 - episode / NUM_EPISODES)
while state != tuple(target_position):
action = choose_action(state, epsilon)
# max와 min 함수는 에이전트가 그리드 월드 환경 내에서 벗어나지 않도록 하기 위해 사용
if action == 0: # 상 : 현재 행을 1 감소시킴 (위쪽으로 이동)
next_state = (max(state[0] - 1, 0), state[1])
elif action == 1: # 하 : 현재 행을 1 증가시킴 (아래쪽으로 이동)
next_state = (min(state[0] + 1, grid.shape[0] - 1), state[1])
elif action == 2: # 좌 : 현재 열을 1 감소시킴 (왼쪽으로 이동)
next_state = (state[0], max(state[1] - 1, 0))
elif action == 3: # 우 : 현재 열을 1 증가시킴 (오른쪽으로 이동)
next_state = (state[0], min(state[1] + 1, grid.shape[1] - 1))
# 보상
# reward = -1 if grid[next_state] != 1 else -100
if grid[next_state] == 1: # 벽을 만났을 때 보상 설정
reward = -(NUM_STATES * 100)
else: # 경로 횟수가 증가될 수록 횟수 만큼 - 보상 (즉 경로 횟수가 적을 수록 보상이 크다)
reward = -(len(path_taken) + 1)
# Q ccc -learning
a1 = Q[state_index(state), action]
a2 = np.max(Q[state_index(next_state)])
q1 = (1 - LEARNING_RATE) * a1
q2 = LEARNING_RATE * (reward + DISCOUNT_FACTOR * a2)
Q[state_index(state), action] = q1 + q2
total_reward += reward
path_taken.append(state)
state = next_state
# 에피소드 다음 배수마다 이동경로 및 순서 출력
if (episode + 1) % 100 == 0:
plt.figure(2)
plt.clf() # Matplotlib의 현재 활성화된 그림 창을 지우기
plt.title(f"Episode : {episode + 1}")
plot_grid_world(state, path_taken)
plt.pause(0.01)
episode_rewards.append(total_reward)
# 에피소드 다음 배수마다 이동경로 및 순서 출력
if (episode + 1) % 10 == 0:
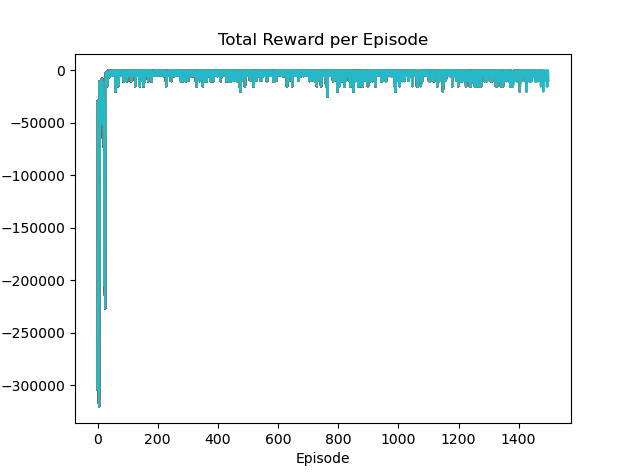
plt.figure(1)
plt.plot(episode_rewards)
plt.xlabel("Episode")
plt.ylabel("Total Reward")
plt.title("Total Reward per Episode")
plt.show()
plt.pause(0.01)
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------
#
# 결과 출력
#
# 학습 완료 후 최적 경로 및 순서 출력
state = tuple(start_position) # 시작 위치
total_reward = 0
best_trajectory = [state] # 최적 경로 및 순서를 저장할 리스트
# 최적 경로 추적
# max와 min 함수는 에이전트가 그리드 월드 환경 내에서 벗어나지 않도록 하기 위해 사용
while state != tuple(target_position):
action = np.argmax(Q[state_index(state)])
if action == 0: # 상 : 현재 행을 1 감소시킴 (위쪽으로 이동)
state = (max(state[0] - 1, 0), state[1])
elif action == 1: # 하 : 현재 행을 1 증가시킴 (아래쪽으로 이동)
state = (min(state[0] + 1, grid.shape[0] - 1), state[1])
elif action == 2: # 좌 : 현재 열을 1 감소시킴 (왼쪽으로 이동)
state = (state[0], max(state[1] - 1, 0))
elif action == 3: # 우 : 현재 열을 1 증가시킴 (오른쪽으로 이동)
state = (state[0], min(state[1] + 1, grid.shape[1] - 1))
best_trajectory.append(state)
# 보상
# reward = -1 if grid[next_state] != 1 else -100
if grid[next_state] == 1: # 벽을 만났을 때 보상 설정
reward = -(NUM_STATES * 100)
else: # 경로 횟수가 증가될 수록 횟수 만큼 - 보상 (즉 경로 횟수가 적을 수록 보상이 크다)
reward = -(len(path_taken) + 1)
total_reward += reward
# 최적 경로 및 순서 출력
plt.figure(3) # 자동으로 크기 조정됨, 새로운 창으로 출력
plt.clf() # Matplotlib의 현재 활성화된 그림 창을 지우기
plt.title(f"Total Reward : {total_reward}, Best Trajectory Length : {len(best_trajectory)}")
plot_grid_world(state, best_trajectory)
plt.show(block=True) # 그래프를 출력한 후 버튼을 누를 때까지 대기
# 결과 로그 출력
print("Learned Q-values:")
print(Q)

반응형
'개발 > AI,ML,ALGORITHM' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Simple Neural Network XOR (0) | 2023.08.29 |
|---|---|
| SARSA (0) | 2023.08.28 |
| MNIST - TensorFlowLite (0) | 2023.07.19 |
| MNIST - Keras (0) | 2023.07.19 |
| MNIST - RandomForestClassifier (0) | 2023.07.19 |
